Connected Devices in Clinical Trials: Adoption Continues to Advance

A YPrime Blog By:
Aubrey Verna,
Senior Product Director
The integration of connected devices in clinical trials enhances clinical research, elevating data collection, patient engagement, and overall study efficiency. As the demand for faster and more reliable clinical outcomes grows, adopting these technologies is becoming more prevalent.
Connected Devices Commonly Used in Clinical Trials
The use of connected devices in clinical research programs has increased steadily since 2014,1 and YPrime research conducted in 2024 indicates that connected devices are now utilized in more than one-third (36%) of studies.2 Projected continued growth reflects the increasing recognition of the value of connected devices in clinical research as they transition from an innovative option to a standard component of clinical trial design.
Regulatory Recognition
Regulatory bodies have validated the importance of connected devices in clinical trials. In September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released its final guidance on Conducting Clinical Trials With Decentralized Elements,3 which recognizes the significance of digital health technologies (DHTs) in clinical research. The FDA term “DHT” encompasses connected devices, and the guidance stipulates that “DHTs may allow transmission of data remotely and securely from trial participants wherever they are located.” The guidance also underscores the potential of DHTs to enable broader clinical trial participation and improve data collection—all while addressing considerations for their implementation in decentralized trials.
Benefits of Connected Devices
The benefits of incorporating connected devices into clinical trials are manifold:
Therapeutic Area Adoption Patterns
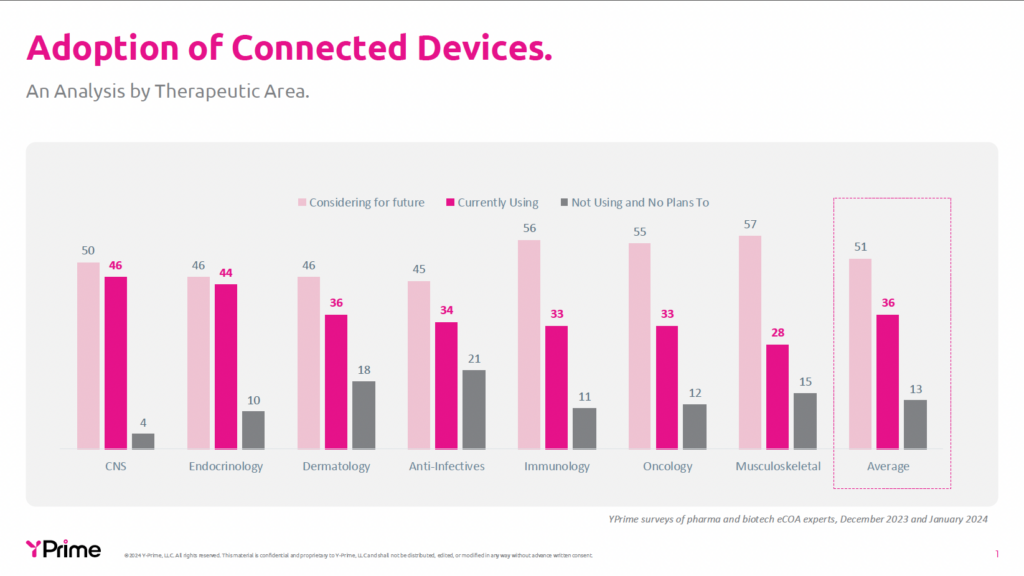
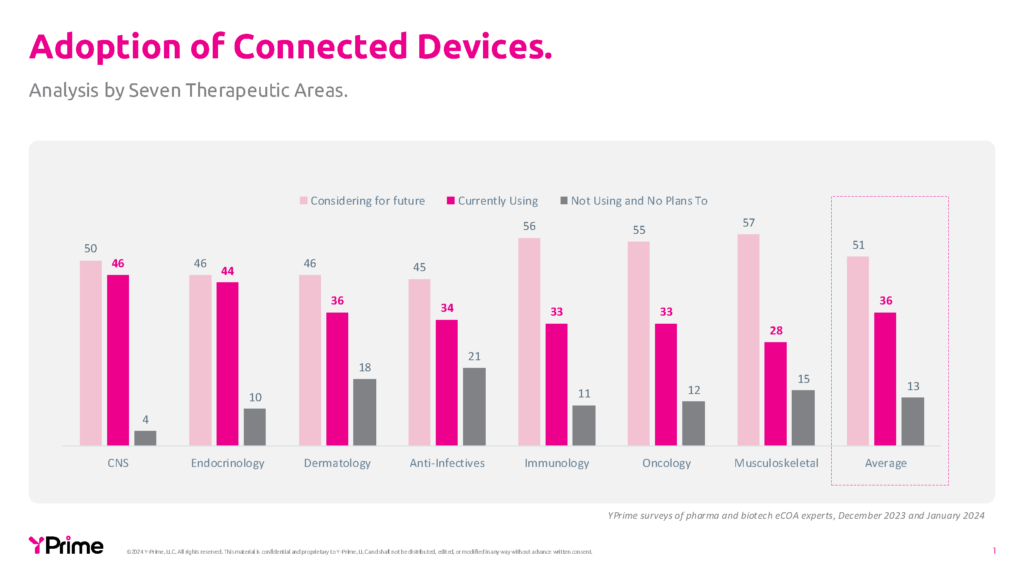
Connected devices demonstrate varying levels of adoption across different therapeutic areas, with some showing more natural alignment than others. In 2024, YPrime conducted a comprehensive survey of 700 pharmaceutical and biotech clinical trial professionals across seven therapeutic areas to understand the adoption patterns of wearables and sensors. The data reveals interesting variations, as depicted in the chart below. Across all therapeutic areas, there is significant current usage (28-46%) and even higher consideration rates (45-57%), with an average of only 13% reporting they are not currently using and have no plans to use connected devices.2
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advantages, adopting connected devices in clinical trials is not without challenges. Issues such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory hurdles, and the complexities involved in managing IoT technologies can pose significant barriers. Sponsors and clinical research organizations (CROs) must carefully select vendors capable of navigating these complexities to ensure successful implementation. Additionally, while many patients appreciate the convenience offered by remote monitoring technologies, some may face difficulties adapting to new devices or may have concerns about data privacy.
YPrime’s Approach to Connected Devices
YPrime is driving this trend, offering innovative solutions for integrating connected devices into their electronic clinical outcome assessment (eCOA) system. Our strategy involves leveraging a data integration platform to connect with numerous devices and applications, collecting user-generated data efficiently and securely.
The process works by extracting data from various connected devices and applications, then de-identifying and converting it into a standardized format. This data is then provided in a JSON format, ensuring that our application receives a predictable, HIPAA/Safe Harbor/PHI-compliant data source—regardless of the connected application or device.
This approach not only streamlines data collection but also ensures compliance with data privacy regulations, addressing one of the key challenges in the adoption of connected devices in clinical trials.
Further Expansion for New Opportunities
The current state of connected devices in clinical trials highlights a pivotal shift toward more efficient and patient-centered research methodologies. As technology advances and the healthcare landscape evolves, the role of connected devices will likely expand further, offering new opportunities for improving patient outcomes and accelerating drug development processes. With regulatory bodies like the FDA acknowledging their importance and companies like YPrime leading the way in implementation, the future appears promising as stakeholders embrace these innovations to enhance the quality and efficiency of clinical trials worldwide.
CITATIONS
1 Guo, Phd, Christine. Why Wearable DHTs are Bringing More Meaningful Data Collection to Patient-Centric Clinical Trials. Applied Clinical Trials. November 7, 2023. https://www.appliedclinicaltrialsonline.com/view/why-wearable-dhts-are-bringing-more-meaningful-data-collection-to-patient-centric-clinical-trials. Accessed December 6, 2024.
2 Bustos, Drew and Rehm, Terry. A Sponsor’s Guide to Leveraging Site Insights for Smarter Technology Decisions. September 2024. https://www.yprime.com/on-demand-webinar-boost-clinical-trials-by-aligning-tech-with-user-needs/. Accessed December 6, 2024.
3 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Guidance Document. Conducting Clinical Trials With Decentralized Elements. September 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/conducting-clinical-trials-decentralized-elements. Accessed December 6, 2024.
4 Anderson, Dawn, Chang, Christine, Lesser, Neil, Overman, Jessica, and Younossi, Alexandria. Broadening clinical trial participation to improve health equity. Deloitte Insights. October 4, 2022. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/health-care/increasing-diversity-clinical-trials.html. Accessed December 6, 2024.
The integration of connected devices in clinical trials enhances clinical research, elevating data collection, patient engagement, and overall study efficiency. As the demand for faster and more reliable clinical outcomes grows, adopting these technologies is becoming more prevalent.
Connected Devices Commonly Used in Clinical Trials
The use of connected devices in clinical research programs has increased steadily since 2014,1 and YPrime research conducted in 2024 indicates that connected devices are now utilized in more than one-third (36%) of studies.2 Projected continued growth reflects the increasing recognition of the value of connected devices in clinical research as they transition from an innovative option to a standard component of clinical trial design.
Regulatory Recognition
Regulatory bodies have validated the importance of connected devices in clinical trials. In September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released its final guidance on Conducting Clinical Trials With Decentralized Elements,3 which recognizes the significance of digital health technologies (DHTs) in clinical research. The FDA term “DHT” encompasses connected devices, and the guidance stipulates that “DHTs may allow transmission of data remotely and securely from trial participants wherever they are located.” The guidance also underscores the potential of DHTs to enable broader clinical trial participation and improve data collection—all while addressing considerations for their implementation in decentralized trials.
Benefits of Connected Devices
The benefits of incorporating connected devices into clinical trials are manifold:
Therapeutic Area Adoption Patterns
Connected devices demonstrate varying levels of adoption across different therapeutic areas, with some showing more natural alignment than others. In 2024, YPrime conducted a comprehensive survey of 700 pharmaceutical and biotech clinical trial professionals across seven therapeutic areas to understand the adoption patterns of wearables and sensors. The data reveals interesting variations, as depicted in the chart below. Across all therapeutic areas, there is significant current usage (28-46%) and even higher consideration rates (45-57%), with an average of only 13% reporting they are not currently using and have no plans to use connected devices.2
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advantages, adopting connected devices in clinical trials is not without challenges. Issues such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory hurdles, and the complexities involved in managing IoT technologies can pose significant barriers. Sponsors and clinical research organizations (CROs) must carefully select vendors capable of navigating these complexities to ensure successful implementation. Additionally, while many patients appreciate the convenience offered by remote monitoring technologies, some may face difficulties adapting to new devices or may have concerns about data privacy.
YPrime’s Approach to Connected Devices
YPrime is driving this trend, offering innovative solutions for integrating connected devices into their electronic clinical outcome assessment (eCOA) system. Our strategy involves leveraging a data integration platform to connect with numerous devices and applications, collecting user-generated data efficiently and securely.
The process works by extracting data from various connected devices and applications, then de-identifying and converting it into a standardized format. This data is then provided in a JSON format, ensuring that our application receives a predictable, HIPAA/Safe Harbor/PHI-compliant data source—regardless of the connected application or device.
This approach not only streamlines data collection but also ensures compliance with data privacy regulations, addressing one of the key challenges in the adoption of connected devices in clinical trials.
Further Expansion for New Opportunities
The current state of connected devices in clinical trials highlights a pivotal shift toward more efficient and patient-centered research methodologies. As technology advances and the healthcare landscape evolves, the role of connected devices will likely expand further, offering new opportunities for improving patient outcomes and accelerating drug development processes. With regulatory bodies like the FDA acknowledging their importance and companies like YPrime leading the way in implementation, the future appears promising as stakeholders embrace these innovations to enhance the quality and efficiency of clinical trials worldwide.
CITATIONS
1 Guo, Phd, Christine. Why Wearable DHTs are Bringing More Meaningful Data Collection to Patient-Centric Clinical Trials. Applied Clinical Trials. November 7, 2023. https://www.appliedclinicaltrialsonline.com/view/why-wearable-dhts-are-bringing-more-meaningful-data-collection-to-patient-centric-clinical-trials. Accessed December 6, 2024.
2 Bustos, Drew and Rehm, Terry. A Sponsor’s Guide to Leveraging Site Insights for Smarter Technology Decisions. September 2024. https://www.yprime.com/on-demand-webinar-boost-clinical-trials-by-aligning-tech-with-user-needs/. Accessed December 6, 2024.
3 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Guidance Document. Conducting Clinical Trials With Decentralized Elements. September 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/conducting-clinical-trials-decentralized-elements. Accessed December 6, 2024.
4 Anderson, Dawn, Chang, Christine, Lesser, Neil, Overman, Jessica, and Younossi, Alexandria. Broadening clinical trial participation to improve health equity. Deloitte Insights. October 4, 2022. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/health-care/increasing-diversity-clinical-trials.html. Accessed December 6, 2024.
Check Out Our Other eCOA Resources
about trial design, data capture, operational efficiencies, and, ultimately, solving for certainty in clinical research.